Remote assistance vs. remote desktop: what’s the difference?
Industry professionals often confuse remote assistance vs. remote desktop. Data managers and IT technicians often use the terms interchangeably, but there are subtle differences between them.
Remote assistance platforms allow a third-party access to a remote PC via an invitation link that must be approved by the end user. These platforms are most effective in cases of collaboration.
On the other hand, remote desktop applications are best for scenarios that require unattended access to a particular PC. IT technicians or MSPs can “remote” into a client PC from a satellite location and perform IT fixes without having to visit on-site. The remote user can use the client computer as if it was their own, gaining access to all files and directories.
Comparing remote assistance and remote desktop
While functionality is the primary area where the two platforms differ, other points of contrast exist when comparing a remote desktop connection vs. remote assistance.
Other ways the two platforms differ are as follows:
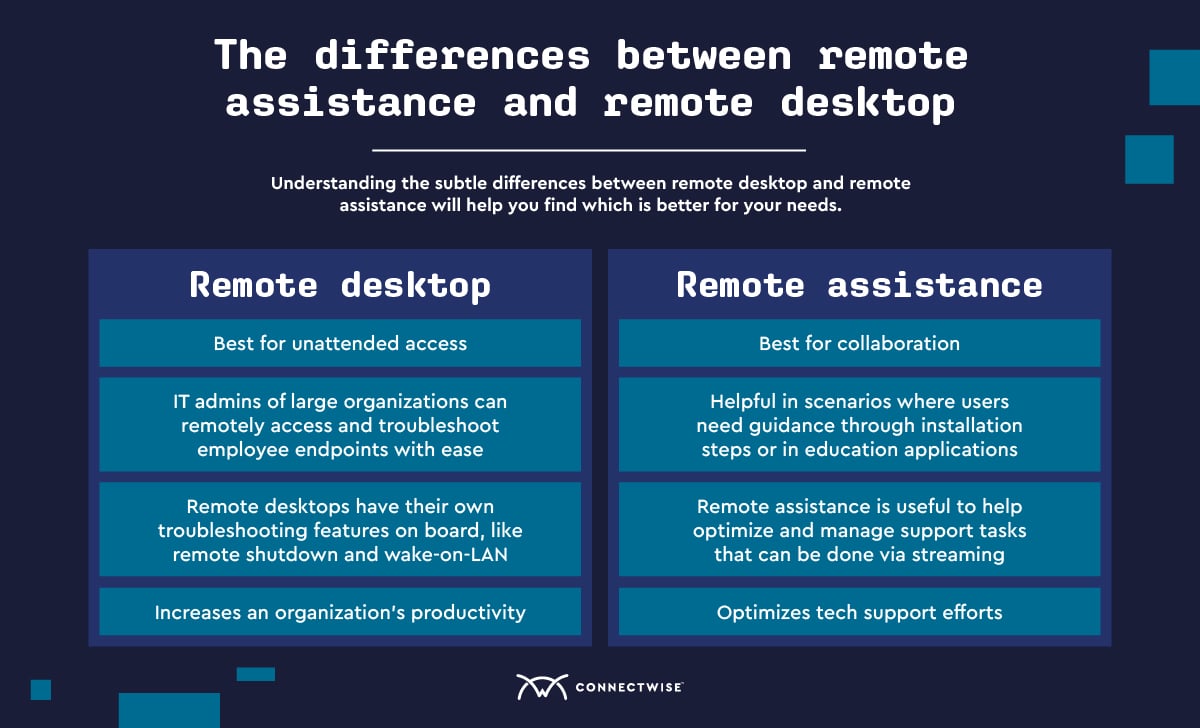
Although remote desktops and remote assistance are similar at their core, we begin to see the differences emerge when we compare them in the table above. Both allow for remote access and involve sharing the target PC’s screen, but their use case scenarios differ distinctly.
Ideal uses for remote assistance
As the name implies, remote assistance platforms are best for situations where a user needs some guidance. This could be to:
- Guide an end-user through software installation
- Instruct a student/new employee via education modules
Ideal uses of remote desktop
Remote desktops are meant for productivity rather than tech support. These platforms facilitate the access of important files, documents, or software from other areas of the network.
An example would be using powerful software within an organization’s network. End users may need to use software that requires much more storage and memory on a larger computer. Since their machine couldn’t handle the application, accessing it via remote desktop allows them to accomplish the work they need to do without crashing their machine.
One important thing to note is that when users access another computer via remote desktop, that computer is no longer online. The screen will go black or freeze, and only the remote user has access. On the other hand, allowing both partners to see the same screen is a critical component of remote assistance, which is why it is best-suited for collaboration.
To learn more about how both remote assistance and remote desktop applications fit into the overall managed services landscape, download our eBook, 10 reasons why you need a reliable remote control solution.
Remote assistance vs. remote desktop: what are the benefits?
As MSPs, leveraging the proper tools can make your job easier and allow you to scale your growing business. By detailing the benefits of remote assistance vs. remote desktop, your team will be able to make the right choice for your own organizational structure and clients. Let’s take a look down below.
Benefits of remote desktop
Remote desktop apps have the following benefits:
- Low cost. Remote desktop platforms can be a budget-friendly solution for IT troubleshooting. Some OS platforms, like Windows, have a remote desktop feature built in. It’s free to Windows users. Third-party apps may also be budget-friendly, depending on the features you and your team need.
- Simple setup and deployment. Setup is as simple as installing the application, and deployment requires establishing a connection with the target computer. Establishing a connection also doesn’t require any additional permissions.
Benefits of remote assistance
In the case of remote assistance, the advantages are:
- Increase efficiency. Most support issues can be resolved with a remote solution. Leveraging remote assistance allows MSPs to resolve issues more efficiently and, as a result, handle many client issues. This is a crucial benefit as you look to grow your MSP business.
- Lower response times. Modern business requires speedy IT solutions. Remote assistance allows for almost immediate troubleshooting of tech challenges. A crucial software settings change, patch, or update can be installed in real time, and both the end user and technician can get back to more important tasks right away.
- Boost revenue. Having your team make in-person calls to clients for their IT needs will require extra expenses. It’s much easier to sell your services without the inflated price tag associated with technician travel expenses, in addition to their skilled labor and expertise. No additional travel expenses means no additional costs and lower prices for your customers, making your MSP services easier to sell.
How MSPs can find the right remote support for them
Ultimately, choosing a remote assistance vs. remote desktop application is going to come down to your organization’s individual needs. Start with the end in mind and ask yourself, “How will I use this tool?” From there, you’ll uncover the necessary features of the ideal remote solution for your business.
When it comes to remote solutions, you want something that you can trust, and at ConnectWise, we understand. Take advantage of our free 14-day trial of ConnectWise ScreenConnect, no credit card required, and see firsthand how it can help you deliver the support your customers need. We are here to answer your questions and help at every step of the way.
